Understanding Food Preservatives: What You Need to Know
03 Oct 2023
Nowadays, modern food production relies on food preservatives to maintain freshness, safety, and shelf stability. Food preservative is defined by Food Act 1983 as any substance that, when added to food, is capable of inhibiting, retarding, or arresting the process of decomposition, fermentation, or acidification of such food.
Food preservatives used are natural (e.g., salt, sugar, honey, vinegar, citric acid) and synthetic/chemical preservatives (e.g., sulphites, benzoates, sorbates). Food preservatives are classified into several main type based on their mechanisms of action and purposes:
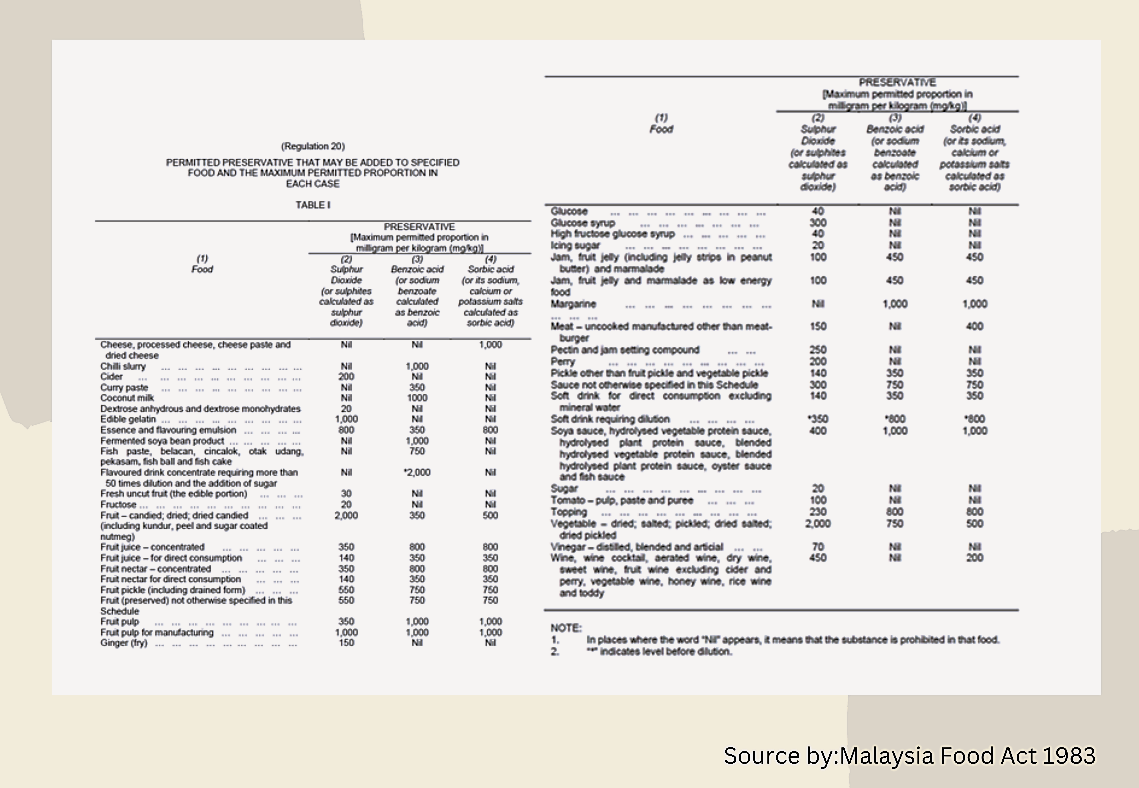
Food preservative dosage varies based on food items and type of preservative. Malaysia's Food Act 1983 outlines permitted preservatives and maximum proportions, as shown below:

It is important to note that while food preservatives offer these benefits, there is a Food Amendment (No.4) Regulation 2020 in Food Act 1983 on how to labelling these preservative on the food packaging to enable consumers to make informed choices regarding foods containing preservatives. Legislation stipulates that additives are labelled by their functional class (preservative, color, antioxidant, etc.) with either their name or INS number in bracket. Regulator continually accesses and monitor the preservative to ensure they are safe for consumption and in acceptable limits.
Food preservatives used are natural (e.g., salt, sugar, honey, vinegar, citric acid) and synthetic/chemical preservatives (e.g., sulphites, benzoates, sorbates). Food preservatives are classified into several main type based on their mechanisms of action and purposes:
| Type of preservatives | Functions | Example |
| Antimicrobial | Inhibit the growth of microorganisms in food products |
-Benzoates (INS 210-INS 213) -Sorbates (INS 200-INS 203) |
| Antioxidants | Prevent or slow down the oxidation of fats and oils, which can lead to rancidity and off-flavors in food products. |
-Ascorbic acid (INS 300) -Tocopherol (INS 307a-INS 307c) |
| Acidulants | Lower the pH of foods, creating an acidic environment that inhibits the growth of microorganisms. |
-Citric Acid (INS 330) -Acetic acid (INS 260) |
| Antimicrobial & Antioxidant | Prevent browning in fruits and vegetables and to inhibit the growth of certain microorganisms | -Sulphites (INS 220-INS 225) |
Food preservative dosage varies based on food items and type of preservative. Malaysia's Food Act 1983 outlines permitted preservatives and maximum proportions, as shown below:


It is important to note that while food preservatives offer these benefits, there is a Food Amendment (No.4) Regulation 2020 in Food Act 1983 on how to labelling these preservative on the food packaging to enable consumers to make informed choices regarding foods containing preservatives. Legislation stipulates that additives are labelled by their functional class (preservative, color, antioxidant, etc.) with either their name or INS number in bracket. Regulator continually accesses and monitor the preservative to ensure they are safe for consumption and in acceptable limits.

